-
Templates
1099 FormsAccurately report 1099 information returns and ensure IRS filing with easeExplore all templatesW-9 W-8 FormsEasily manage and share taxpayer details to streamline payments and meet IRS requirements with confidenceExplore all templatesOther Tax FormsFillable tax forms simplify and speed up your tax filing process and aid with recordkeeping.Explore all templatesReal EstateReal estate templates for all cases, from sale to rentals, save you a lot of time and effort.Explore all templatesLogisticsSimplify your trucking and logistics paperwork with our ready-to-use transportation and freight templates.Explore all templatesMedicalMedical forms help you keep patient documentation organized and secure.Explore all templatesBill of SaleBill of Sale templates streamline the transfer of ownership with clarity and protection.Explore all templatesContractsVarious contract templates ensure efficient and clear legal transactions.Explore all templatesEducationEducational forms and templates enhance the learning experience and student management.Explore all templates
-
Features
FeaturesAI-Enhanced Document Solutions for Contractor-Client Success and IRS ComplianceExplore all featuresAI Summarizer Check out the featureAI PDF summarizer makes your document workflow even faster. Ask AI to summarize PDF, assist you with tax forms, complete assignments, and more using just one tool.Sign PDF Check out the featurePDFLiner gives the opportunity to sign documents online, save them, send at once by email or print. Register now, upload your document and e-sign it onlineFill Out PDF Check out the featurePDFLiner provides different tools for filling in PDF forms. All you need is to register, upload the necessary document and start filling it out.Draw on a PDF Check out the featureDraw lines, circles, and other drawings on PDF using tools of PDFLiner online. Streamline your document editing process, speeding up your productivity
- Solutions
- Features
- Blog
- Support
- Pricing
Register as an Independent Contractor: Comprehensive Guide
.png)
Dmytro Serhiiev
Becoming an independent contractor can offer you freedom and flexibility to shape your career on your terms. Whether you're venturing into freelancing or starting a consulting business, this article will provide you with vital steps and valuable tips to navigate the path toward becoming a successful independent contractor.

What Is a 1099 Independent Contractor?
A 1099 independent contractor is an individual or business entity hired by another party to perform specific tasks or services on a freelance or contractual basis. Unlike traditional employees, independent contractors work autonomously, often setting their own hours and using personal tools to complete projects. The term ‘1099’ is related to the IRS tax form (Form 1099-NEC) that is used to report income earned by independent contractors.
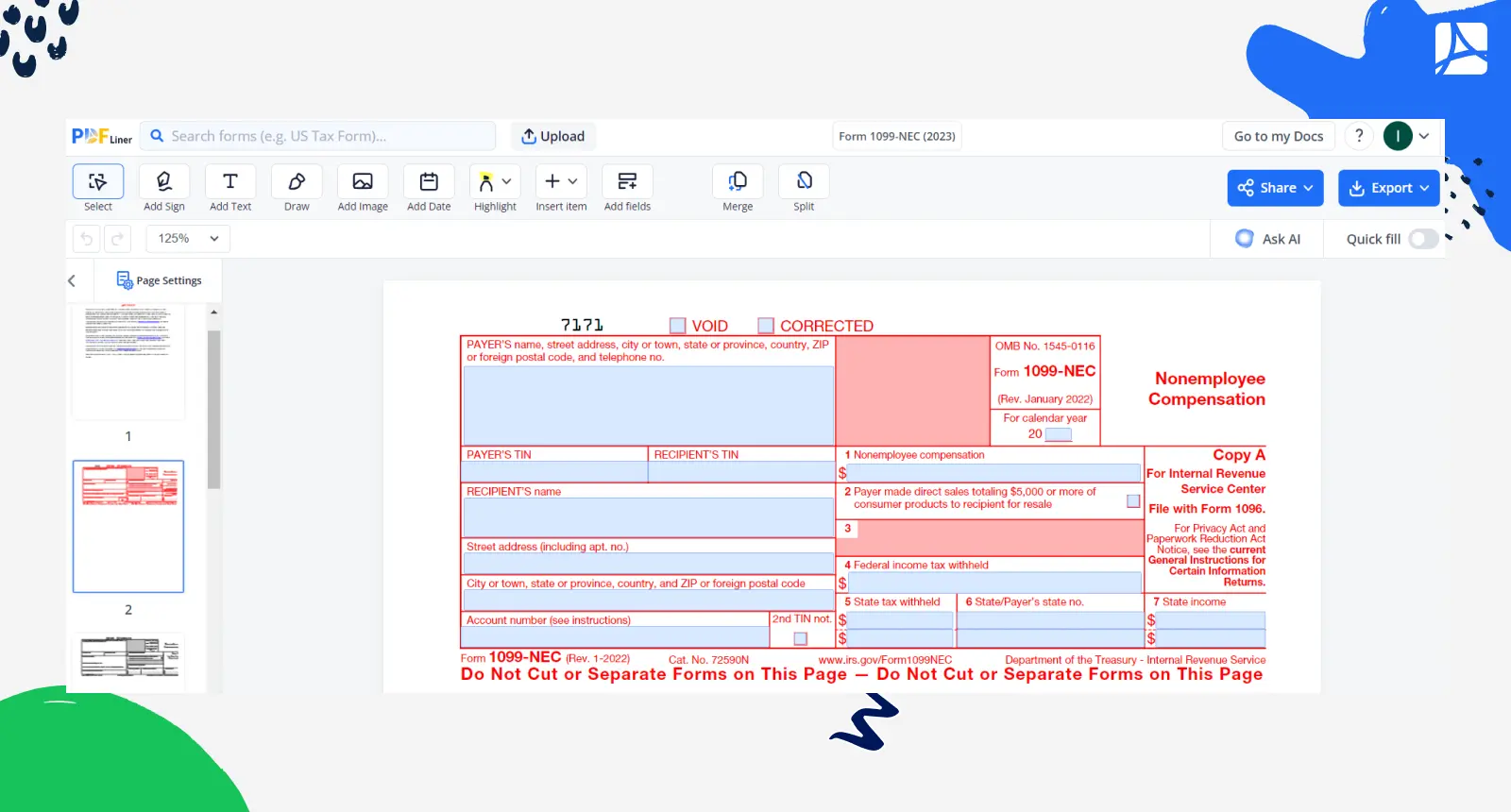
Being an independent contractor comes with an array of perks. Find them below:
- Flexibility & Autonomy. Independent pros have the freedom to choose their working hours and projects, allowing for a better work-life balance.
- Variety of Clients. Contractors can work with multiple clients simultaneously, diversifying their income sources.
- Tax Benefits. They can deduct business-related expenses from their taxable income, potentially lowering their tax liability.
- Higher Earning Potential. Independent contractors often have the potential to earn more than traditional employees, especially in specialized fields.
Alas, being an independent contractor also comes with certain drawbacks. Find them below:
- Unstable Income. Income can fluctuate, making it challenging to budget and save.
- No Benefits. Independent contractors typically don't receive benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, or paid time off.
- Self-Employment Taxes. They are responsible for paying self-employment taxes, which can be higher than regular payroll taxes.
- Administrative Burden. Contractors must handle their own bookkeeping, invoicing, and tax compliance, which can be time-consuming.
How to Become an Independent Contractor
How do I become a 1099 independent contractor? If this question has been lingering in your mind for some time, we’ve got you covered. Here are 9 vital steps to guide your way into the world of freelancing and contracting.

Step 1. Select the right business type
The first crucial step is to determine your business structure. You have several options, including:
- Sole Proprietorship. The simplest structure, where you and your operation are one entity. Easy to set up, but you're personally liable for business debts.
- LLC. Offers personal liability protection while maintaining simplicity in management and taxation.
- S Corporation. Suitable for larger operations, with potential tax advantages but more administrative complexity.
- C Corporation. Often used for substantial enterprises, offering legal separation between owners and businesses but with more regulatory requirements.
Step 2. Get a Tax ID Number
The second step in becoming a 1099 independent contractor involves obtaining a Tax Identification Number (TIN) or an Employer Identification Number (EIN). This unique identifier is one of the answers to your ‘What do I need to be an independent contractor?’ question. It’s essential for tax purposes and helps distinguish your business entity from your personal finances.
If you're a sole proprietor, you can use your Social Security Number as your TIN. However, for other business structures like LLCs or corporations, an EIN is necessary. Obtaining a TIN or EIN is typically a straightforward process, and it enables you to establish a dedicated business bank account and fulfill your tax obligations accurately.
Step 3. Register your business name
This process involves officially declaring the name under which you'll operate your freelance or contracting endeavors. Depending on your location and business structure, you might need to file a ‘Doing Business As’ (DBA) or fictitious business name registration.
Registering your business name is essential not only for legal compliance but also for establishing your professional identity. It enables you to conduct transactions and contracts under your chosen business name, adding credibility and recognition to your independent contracting career.
Step 4. Open a separate business account
This step ensures a clear separation between your personal and business finances, simplifying bookkeeping and financial management. By having a separate business account, you can accurately monitor income and expenses related to your contracting work. Upon exploring the types of business bank accounts and choosing your business type, research banks based on such criteria as fees, account features, and accessibility. Pick the most suitable bank for your needs. Then visit this bank and discuss account options with its representatives.
After that, fill out the necessary account application forms and provide the requested documentation. Finalize the process by making an initial deposit into your new business account. From this point forward, use your business account exclusively for business-related transactions, helping you maintain clear financial separation.
Step 5. Organize documents and records
Effectively managing your documents and records is a vital aspect of being an independent contractor. To do it effectively:
- Begin by setting up a digital filing system. Use cloud-based platforms like Google Drive or PDFLiner to store, edit, and share invoices, contracts, and receipts securely.
- Organize these documents chronologically or by project, and maintain consistent naming conventions for files.
- Keep meticulous records of your income and expenses, using software like QuickBooks or Excel spreadsheets.
- Separate tax-related documents, such as 1099 forms, editable W9 forms to send yor clients and receipts for deductible expenses, from your general records.
- Regularly update and review your records, dedicating time each month to ensure accuracy. This proactive approach simplifies tax filing and helps you stay on top of your financial situation.
Step 6. Create your standard contract template
Design a comprehensive agreement that records project scope, timelines, payment terms, and expectations. Ensure it includes clauses for intellectual property rights, confidentiality, and dispute resolution. Tailor the template to your specific industry and services but keep it flexible for customization as needed for each client. A well-structured contract not only protects your interests but also fosters professionalism and trust with clients, setting the stage for successful collaborations.
Step 7. Get an invoice template (if needed)
Having a professional invoice template is essential for billing clients accurately and efficiently. While you can create one from scratch, consider using a ready-made template to save time and ensure correctness. You can find a multitude of niche-specific document templates, including invoice templates, in the PDFLiner file catalog.
These forms often come preformatted and tailored for various industries, making it easier to include essential details such as your contact information, payment terms, and itemized services. A well-designed invoice template is a useful document to maintain organized financial records, especially when tax time comes and you need to provide 1099 forms for independent contractors.
Step 8. Purchase insurance
Invest in insurance coverage tailored to your contracting work. Start with general liability insurance to protect against lawsuits and accidents. Consider professional liability insurance if your work involves providing advice or services. Additionally, health insurance is vital, as independent contractors don't receive benefits. Assess your specific needs and consult an insurance agent to find suitable coverage options and ensure financial security in case of unforeseen events.
Step 9. Market your services
This step is paramount for attracting clients. Build an online presence via a well-thought-out website and social media profiles. Showcase your expertise through blog posts, videos, or case studies. Network within your niche and attend relevant activities. Offer promotions or discounts to entice new clients. Consistent marketing efforts can help you establish a strong client base and sustain a successful independent contracting career. That’s pretty much it when it comes to the basics of how to become an independent contractor.
Create W-9 Template 65f013686d1834a70e07c82d
Tips For Becoming a 1099 Independent Contractor
Here are some more tips from our experts on how to become a self-contractor:

1. Maintain financial discipline
Keep meticulous financial records, set aside funds for taxes, and seek guidance from financial professionals for tax planning and management.
2. Stay informed about tax laws
Continuously educate yourself about tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and minimize tax liabilities.
3. Seek legal and financial advice
Consult with lawyers and accountants to ensure that your business structure, contracts, and financial practices are legally sound.
4. Plan for retirement
Explore retirement account options like a Solo 401(k) or SEP IRA to secure your financial future.
5. Invest in upskilling
On average, your skill half-lives for five years, as per a fairly recent study. With that said, five years from now, what you’re brilliant at will be half as valuable. These overwhelming stats emphasize the importance of investing in ongoing education and training to expand your skills and expertise.
6. Diversify your client base
Avoid overreliance on a single client by diversifying your client portfolio to mitigate financial risks.
7. Create an emergency fund
Set aside funds for emergencies to cover your expenses during lean periods or unexpected setbacks.
8. Maintain work-life balance
Prioritize work-life balance to prevent burnout and ensure sustained success as an independent contractor.
By following these useful additional tips from our business experts, you can navigate the journey of becoming a 1099 independent contractor successfully and build an exciting freelance career.
FAQ
Do you need a license to be an independent contractor?
Not always. Licensing requirements for independent contractors vary by location and profession. In many cases, you might not need a specific license to operate as an independent contractor. However, it's crucial to check this issue with your local government and industry regulations to ensure compliance with any licensing or permit obligations that may apply to your specific line of work.
What to know about being an independent contractor?
In a nutshell, being an independent contractor involves considerations like tax responsibilities, setting your rates, managing your finances, and securing insurance coverage. You'll also need to create clear contracts, market your services, and maintain a work-life balance. Staying informed about legal and industry-specific requirements is crucial for a successful independent contracting career.
Do I have to pay self-employment taxes as a 1099 employee?
Yes, as a 1099 independent contractor, you're responsible for paying self-employment taxes. These include Social Security and Medicare taxes, often referred to as the ‘self-employment tax.’ You'll need to calculate and pay these taxes on your income, usually through quarterly estimated tax payments to the IRS.
Do independent contractors need a business name?
No, independent contractors are not required to have a business name. You can operate under your own legal name as a sole proprietor without registering a separate business name. However, if you wish to use a distinct business name, you might need to register it as a ‘Doing Business As’ (DBA) or fictitious business name, depending on local regulations.
How do I pay taxes as an independent contractor?
As an independent contractor, you pay taxes by estimating and paying your own income and self-employment taxes. This involves calculating your tax liability, making quarterly estimated tax payments to the IRS, and filing an annual tax return, typically using Schedule C or C-EZ to report your income and expenses.
Document Management is Easy with PDFLiner
Stay organized and keep all your PDFs in one place














































.png)